Product Information
Catalog Number:
C1228-1
Lot Number:
C1228-1-121611
Quantity:
1 vial (2 x 106) frozen cells
Freeze Medium:
Sigma Freezing Medium (C-6164)
Host cell:
CHO-K1
Transfection:
Expression vector containing full-length human CRHR1 cDNA (GenBank Accession Number NM_004382.3) with FLAG tag sequence at N-terminus
Recommended Storage:
Liquid nitrogen upon receiving
Propagation Medium: DMEM, 10% FBS, 10 µg/mL puromycin
Stability:
In progress
Data Sheet
Background: Human secretin receptor (gene name SCTR) is a G-protein-coupled receptor, a member of the class B GPCR subfamily. Secretin receptor binds to peptide secretin and the pituitary adenylate cyclase activating peptide. It was the first receptor that was cloned in the class B family of GPCRs. Secretin receptor is also regulated by peptide hormones from the glucagon hormone family. The receptor activates two distinct intracellular signaling pathways, i.e. the adenyl cyclase and the phosphatidyl-inositol calcium pathways. Northern blot analysis has shown that the secretin receptor is expressed in pancreas, kidney, small intestine, lung, liver, and in trace levels in the brain, heart and ovary. Secretin-receptor mRNA is abundant in all gastrinomas, enriched in one specific variant. Knockout of secretin receptor was shown to reduce large cholangiocyte hyperplasia. Studies have also demonstrated the potential use of secretin as a therapy for ductopenic liver diseases.
Application: Functional assays
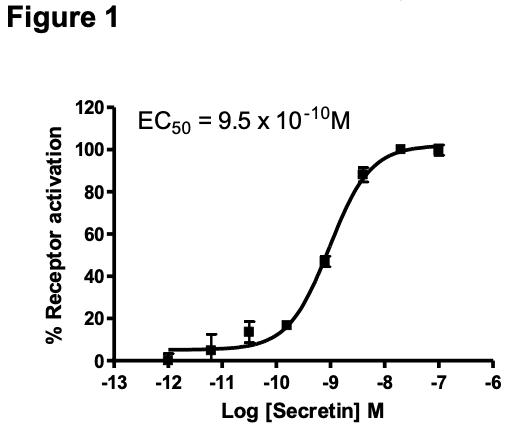
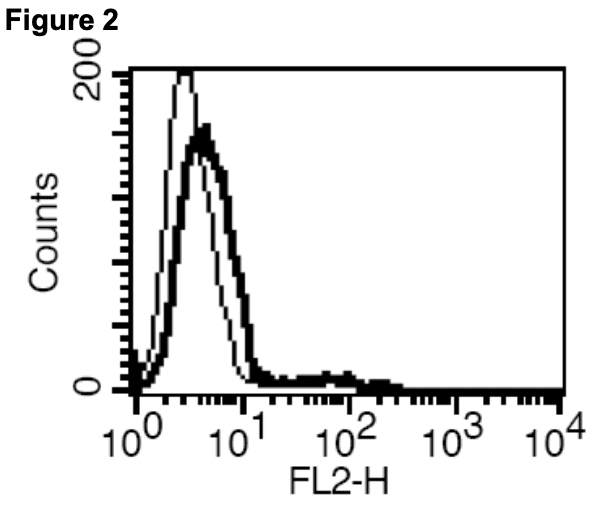
Figure 1. Dose-dependent stimulation of intracellular cAMP level upon treatment with ligand, measured with MultiscreenTM TR-FRET cAMP 1.0 No Wash Assay Kit (Multispan MSCM01). Figure 2. Receptor expression on cell surface measured by flow cytometry (FACS) using an anti-FLAG antibody. Thin line: parental cells; thick line: receptor-expressing cells.
References:
Dong M, Miller LJ. (2002) Molecular pharmacology of the secretin receptor. Receptors Channels 8:189-200.
Glaser S et al. (2010) Knockout of secretin receptor reduces large cholangiocyte hyperplasia in mice with extrahepatic cholestasis induced by bile duct ligation. Hepatology 52:204-214.
Lam IP, Siu FK, Chu JY, Chow BK. (2008) Multiple actions of secretin in the human body. Int Rev Cytol. 265:159-190.
