Product Information
Catalog Number:
C1210-7
Lot Number:
C1210-7-021513
Quantity:
1 vial (2 x 106) frozen cells
Freeze Medium:
Sigma Freezing Medium (C-6164)
Host cell:
Hela
Transfection:
Expression vector containing full-length human PAR4 cDNA (GenBank Accession Number NM_003950.2) with FLAG tag sequence at N-terminus
Recommended Storage:
Liquid nitrogen upon receiving
Propagation Medium: DMEM/F12, 10% FBS, 1X NEAA, 1 µg/mL puromycin
Stability:
Stable in culture for minimum of two months
Data Sheet
Background: Protease-activated receptor 4 (PAR-4) is also known as coagulation factor II (thrombin) receptor-like 3, and is activated by proteolytic cleavage of its extracellular amino terminus by a protease, specifically thrombin or trypsin. In humans, PAR-4 has been shown to be highly expressed in many tissues, and in high levels in the lung, pancreas, thyroid, testis, and small intestine. Thrombin signaling through PARs have been shown to affect many physiological activities such as platelet activation, intimal hyperplasia, inflammation, and maintenance of vascular tone and barrier function. In the blood coagulation process, it has been determined that clot elasticity is decreased significantly when PAR-4 receptor is inhibited. Furthermore, PAR-4 is likely activated by low concentrations of thrombin during the initial phase of thrombin generation and is important for the clotting time, and the PAR-4 receptor may play a role in stabilizing the coagulum.
Application: Functional assays
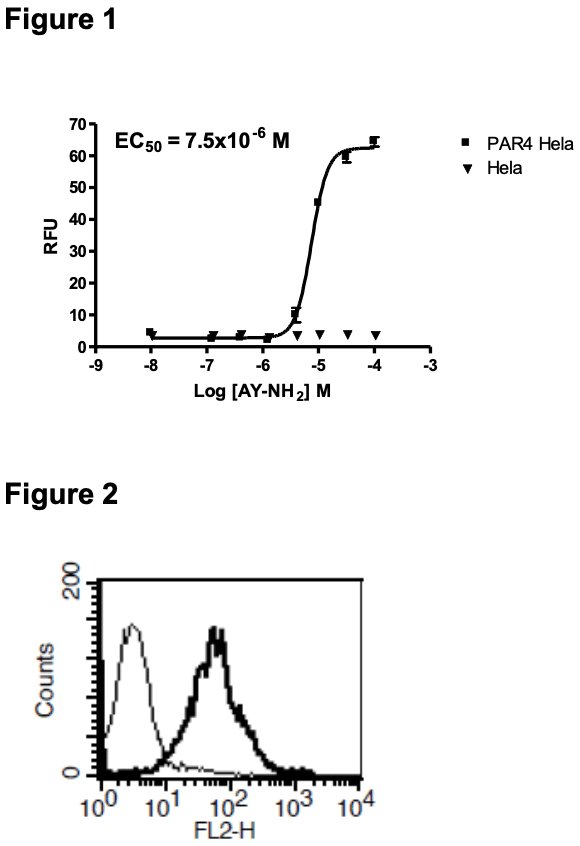
Figure 1. Dose-dependent stimulation of calcium flux upon treatment with ligand, measured with MultiscreenTM Calcium 1.0 No Wash Assay Kit (Multispan MSCA01). Figure 2. Receptor expression on cell surface measured by flow cytometry (FACS) using an anti-FLAG antibody. Thin line: parental cells; thick line: receptor-expressing cells.
References:
Leger, AJ et al. (2006) Protease-activated receptors In cardiovascular diseases. Circulation. 114(10):1070-7.
Xu, WF et al. (1998) Cloning and characterization of human protease-activated receptor 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA v.95(12)
Vretenbrant, K et al. (2007) Platelet activation via PAR4 is involved in the initiation of thrombin generation and in clot elasticity development. Thromb Haemost. 97(3):417-24.
