Product Information
Catalog Number:
CA1350-1a
Lot Number:
CA1350-1a-022718
Quantity:
1 vial (2 x 106) frozen cells
Freeze Medium:
Cellbanker 2
Host cell:
CHO-K1 β-Arrestin2
Transfection:
Expression vector containing full-length human OPRM1 cDNA (GenBank accession number NM_000914.2) with FLAG tag sequence at N-terminus and ARRB2 cDNA (GenBank Accession Number NM_004313.3)
Recommended Storage:
Liquid nitrogen upon receiving
Propagation Medium: DMEM/F12, 10% FBS, 10 μg/mL puromycin, 800 μg/mL G418
Stability:
Stable in culture for minimum of two months
Data Sheet
Background: μ opioid receptor (MOR) is a G protein-coupled receptor for β-endorphin. The receptor activation inhibits neurotransmitter release by reducing calcium currents and increasing potassium conductance. MOR mediates positive reinforcement following direct (morphine) or indirect (alcohol, cannabinoids, nicotine) activation. MOR plays a genetic role in the control of gut inflammation. MOR-deficient mice are highly susceptible to colon inflammation, with a 50% mortality rate occurring 3 days after administration of TNBS that induces inflammation. MOR agonists regulate cytokine production and T cell proliferation and might be new therapeutic molecules in inflammatory bowel disease.
Application: Functional assays
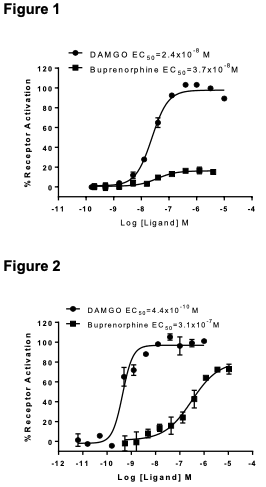
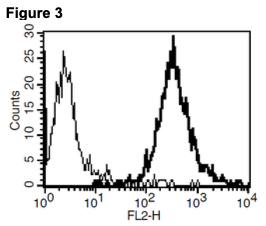
Figure 1. Dose-dependent stimulation from arrestin recruitment upon treatment with ligand, monitored on Flexstation III. Figure 2. Dose-dependent inhibition of forskolin- stimulated intracellular cAMP accumulation upon treatment with ligand, measured with MultiscreenTM TR-FRET cAMP 1.0 No Wash Assay Kit (Multispan MSCM01). Figure 3. Receptor expression on cell surface measured by flow cytometry (FACS) using an anti- FLAG antibody. Thin line: parental cells; thick line: receptor-expressing cells.
References:
Chen et al. (1993) Molecular cloning and functional expression of a mu-opioid receptor from rat brain. Mol Pharmacol 44:8-12.
Contet et al. (2004) Mu opioid receptor: a gateway to drug addiction. Curr Opin Neurobiol 14:370-378.
Philippe et al. (2003) Anti-inflammatory properties of the mu opioid receptor support its use in the treatment of colon inflammation. J Clin Invest 111:1329-1338.
