Product Information
Catalog Number:
MC1048-6
Lot Number:
C1048-6-07122013
Quantity:
9.22mg/ml, 1mg
Host cell:
RH7777
Transfection:
Expression vector containing full-length human LPA1 cDNA (GenBank Accession Number:NM_001401) with FLAG tag sequence at N-terminus
Recommended Storage:
Liquid nitrogen upon receiving
Data Sheet
Background: The lipid growth factor lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is responsible for cell signaling in diverse pathways including survival, proliferation, motility, and differentiation. LPA acts upon target cells by activating its cognate receptors, which belong to the G protein-coupled endothelial differentiation gene (EDG) family. Four mammalian cell surface LPA receptors have been identified so far: EDG-2 (LPA1), EDG-4 (LPA2), EDG-7 (LPA3) and LPA4 (GPR23/P2Y9). EDG-2 is the most widely expressed receptor, with high-level mRNAs in the colons, small intestine, placenta, brain and heart. Heterologous expression studies have shown that EDG-2 couples to both Gi/o and Gq to mediate PLC activation, inhibition of cAMP accumulation and activation of the MAPK pathway. EDG-2 deficient mice show phenotypic changes observed in psychiatric disease as well as impaired suckling behavior attributable to defective olfaction.
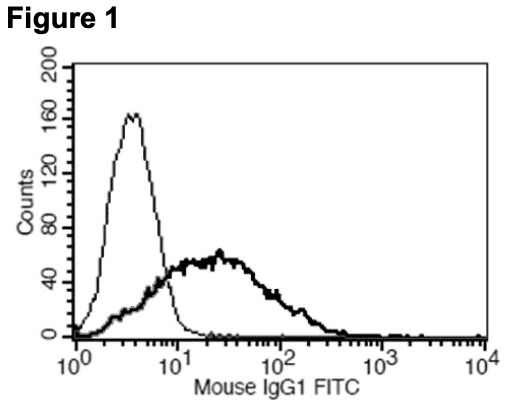
Figure 1. Receptor expression on cell surface measured by flow cytometry (FACS) using an anti-FLAG antibody. Thin line: parental cells; thick line: receptor-expressing cells.
References:
Mills and Moolenaar (2003) The emerging role of lysophosphatidic acid in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 3:582-591.
Yang et al. (2002) In vivo roles of lysophospholipid receptors revealed by gene targeting studies in mice. Biochim Biophys Acta 1582:197-203.
