Product Information
Catalog Number:
Cm1030
Lot Number:
Cm1030-110609
Quantity:
1 vial (2 x 106) frozen cells
Freeze Medium:
Sigma Freezing Medium (C-6164)
Host cell:
HEK293T
Transfection:
Expression vector containing full-length mouse HRH4 cDNA (GenBank Accession Number NM_153087.1) with FLAG tag sequence at N-terminus
Recommended Storage:
Liquid nitrogen upon receiving
Propagation Medium: DMEM, 10% FBS, 1 μg/mL puromycin
Stability:
Stable in culture for minimum of two months
Data Sheet
Background: Histamine is one of the most studied biomolecules in medicine and is most notably known for its effects on smooth muscle contraction, vascular permeability and regulation of stomach acid. The histamine receptor H4 has been shown to have a role in chemotaxis and mediator release in a variety of immune cells, such as mast cells, eosinophils, dendritic cells, and T cells. The development of potent H4 receptor antagonists has great potential to open up the pathway for new therapeutic treatments in chronic inflammatory diseases, such as bronchial asthma, allergic gastrointestinal disease, and atopic dermatitis.
Application: Functional assays
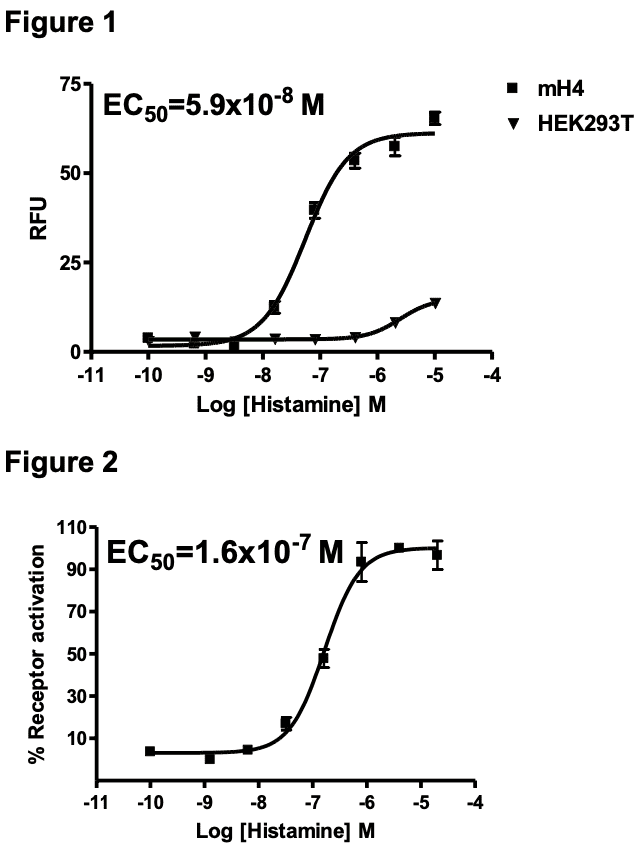
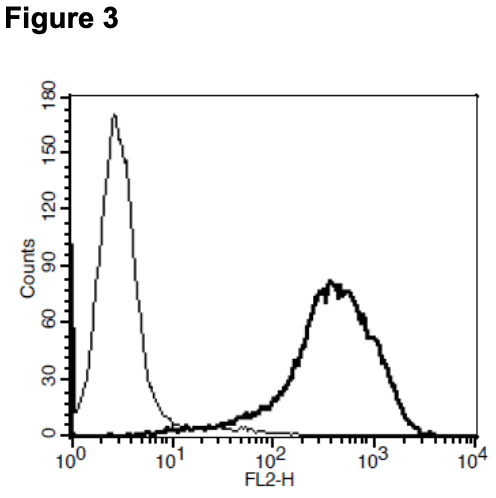
Figure 1. Dose-dependent stimulation of calcium flux upon treatment with ligand, measured with MultiscreenTM Calcium 1.0 No Wash Assay Kit (Multispan MSCA01). Figure 2. Dose-dependent inhibition of forskolin-stimulated intracellular cAMP level upon treatment with ligand, measured with MultiscreenTM TR-FRET cAMP 1.0 No Wash Assay Kit (Multispan MSCM01). Figure 3. Receptor expression on cell surface measured by flow cytometry (FACS) using an anti-FLAG antibody. Thin line: parental cells; thick line: receptor-expressing cells.
References:
Daugherty (2004) Histamine H4 antagonism: a therapy for chronic allergy?. Br J Pharmacol 142:5-7.
Nguyen et al. (2001) Discovery of a novel member of the histamine receptor family. Mol Pharmacol 59:427-433.
Liu et al. (2001) Comparison of human, mouse, rat, and guinea pig histamine receptors reveals substantial pharmacological species variation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 299:121-130.
