Product Information
Catalog Number:
Cm1029
Lot Number:
Cm1029-080712
Quantity:
1 vial (2 x 106) frozen cells
Freeze Medium:
Sigma Freezing Medium (C-6164)
Host cell:
HEK293T
Transfection:
Expression vector containing full-length mouse Hrh3 cDNA (GenBank accession number NM_133849) with FLAG tag sequence at N-terminus
Recommended Storage:
Liquid nitrogen upon receiving
Propagation Medium: DMEM, 10% FBS, 1 μg/mL puromycin
Stability:
In progress
Data Sheet
Background: Histamine is one of the most studied biomolecules in medicine and is most notably known for its effects on smooth muscle contraction, vascular permeability and regulation of stomach acid. The histamine receptor H3 was initially recognized as an autoreceptor controlling histamine synthesis and release in the brain. The inhibition mediated by H3 autoreceptors constitutes a major regulatory mechanism of histaminergic neurons in vivo. Functional and localization studies have shown that H3 receptors are also present on perikarya, dendrites and projections of many other neurones in brain and peripheral tissues. The histamine receptor H3 has been found to prevent oxidative stress and alleviate schizophrenic symptoms, particularly the negative symptoms and cognitive deficits.
Application: Functional assays
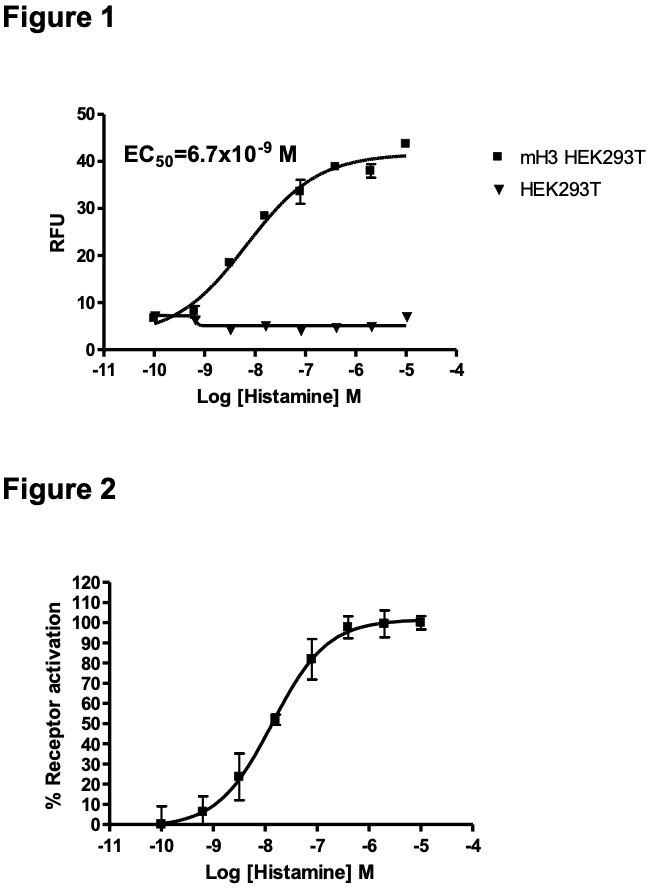
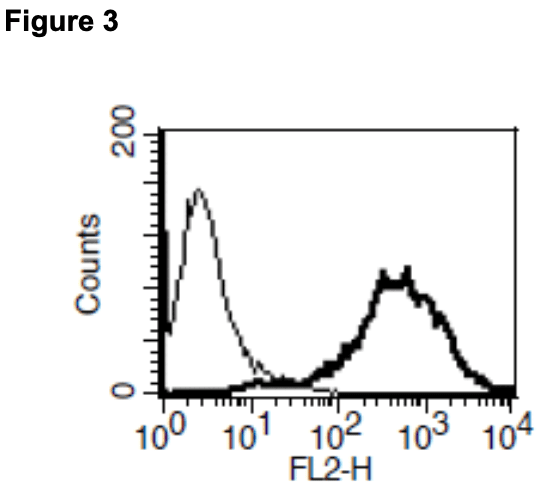
Figure 1. Dose-dependent stimulation of calcium flux upon treatment with ligand, measured with MultiscreenTM Calcium 1.0 No Wash Assay Kit (Multispan MSCA01). Cells were transiently transfected with Gαqi5. Figure 2. Dose-dependent inhibition of forskolin-stimulated intracellular cAMP level upon treatment with ligand, measured with MultiscreenTM TR-FRET cAMP 1.0 No Wash Assay Kit (Multispan MSCM01). Figure 3. Receptor expression on cell surface measured by flow cytometry (FACS) using an anti-FLAG antibody. Thin line: parental cells; thick line: receptor-expressing cells.
References:
Mahmood et al. (2012) Reversal of oxidative stress by histamine H3 receptor-ligands in experimental models of schizophrenia. Arzneimittelforschung 62(05):222-229.
Rouleau, A. et al. (2004) Cloning and expression of the mouse histamine H3 receptor: evidence for multiple isoforms. J Neurochem 90: 1331-1338.
