Product Information
Catalog Number:
DH1099
Lot Number:
12/21/10
Quantity:
1 vial (2 x 106) frozen cells
Freeze Medium:
Sigma Freezing Medium (C-6164)
Host cell:
HEK293T
Transfection:
Expression vector containing full-length human GPR39 cDNA (GenBank Accession Number NM_001508.1) with FLAG tag sequence at N-terminus
Recommended Storage:
Liquid nitrogen upon receiving
Propagation Medium: DMEM, 10% FBS
Stability:
Stable for 1-2 days after thawing
Data Sheet
Background: The G protein-coupled receptor 39 is a seven transmembrane receptor expressed mainly in endocrine and metabolic tissues and is a member of the ghrelin receptor family. The receptor acts as a Zn++ sensor signaling mainly through Gq and G12/13 pathways. It was first reported to be the receptor for a peptide fragment from the ghrelin precursor named obestatin but later it was reported that obestatin did not activate GPR39 and therefore, the natural ligand for GPR39 is uncertain so far. GPR39 is expressed in the stomach, small intestine and areas of the brain, including the hypothalamus. The expression of GPR39 is regulated by hepatocyte nuclear factor (HNF)-1alpha and HNF-4alpha and plays an important role in glucose homeostasis and pancreatic islet functions. Deficiency of the GPR39 receptor is associated with obesity and altered adipocyte metabolism. In addition, it has been shown that overexpression of GPR39 contributes to malignant development of human oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Application: Ca++ assays
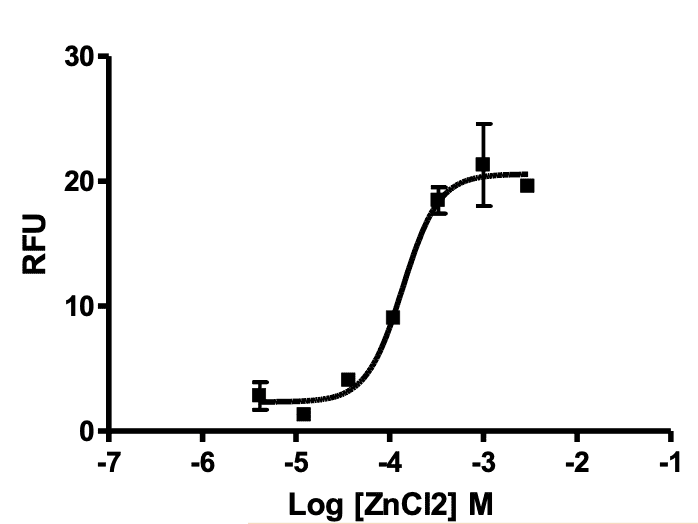
Figure legend: Dose-dependent calcium flux upon treatment with ligand, measured with MultiscreenTM Calcium 1.0 No Wash Assay Kit (Multispan MSCA01).
References:
McKee et al. (1997) Cloning and characterization of two human G protein-coupled receptor genes (GPR38 and GPR39) related to the growth hormone secretagogue and neurotensin receptors. Genomics 46:426-434.
Zhang et al. (2005) Obestatin, a peptide encoded by the ghrelin gene, opposes ghrelin’s effects on food intake. Science 310:996-999.
