Product Information
Catalog Number:
CA1290
Lot Number:
CA1290-072619
Quantity:
1 vial (2 x 106) frozen cells
Freeze Medium:
Cellbanker 2
Host cell:
HEK293T β-Arrestin2
Transfection:
Expression vector containing full-length human GIPR cDNA (GenBank accession number NM_000164) with FLAG tag sequence at N-terminus and ARRB2 cDNA (GenBank Accession Number NM_004313.3)
Recommended Storage:
Liquid nitrogen upon receiving
Propagation Medium: DMEM, 10% FBS, 1 μg/mL puromycin, 250 μg/mL hygromycin
Stability:
In progress
Data Sheet
Background: GIP (gastric inhibitory polypeptide) is released from the gastrointestinal tract, stimulates insulin secretion from pancreatic beta-cells, and plays a crucial role in the regulation of insulin secretion. Its receptor GIPR is expressed in the pancreas, stomach, small intestine, adipose tissue, adrenal cortex, pituitary, heart, testis, endothelial cells, bone, trachea, spleen, thymus, lung, kidney, thyroid, and several regions in the CNS. GIPR may have therapeutic potential in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Application: Functional assays
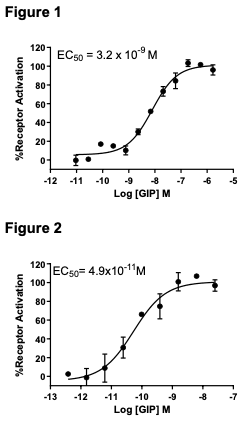
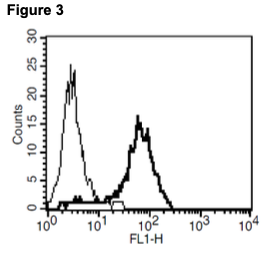
Figure 1. Dose-dependent stimulation from arrestin recruitment upon treatment with ligand, measured with MULTISCREENTM β-Arrestin Assay Kit (Multispan MSBAK01). Figure 2. Dose-dependent stimulation of intracellular cAMP level upon treatment with ligand, measured with MULTISCREENTM TR-FRET cAMP 1.0 No Wash Assay Kit (Multispan MSCM01) Figure 3. Receptor expression on cell surface measured by flow cytometry (FACS) using an anti-FLAG antibody. Thin line: parental cells; thick line: receptor-expressing cells.
References:
Irwin et al. (2009) Therapeutic potential for GIP receptor agonists and antagonists. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 23:499-512.
Yamada et al. (1995) Human gastric ingibitory polypeptide receptor: cloning of the gene (GIPR) and cDNA. Genomics 29:773-776.
