Product Information
Catalog Number:
CAr1230BA2-1
Lot Number:
CAr1230BA2-1-090122
Quantity:
1 vial (2 x 106) frozen cells
Freeze Medium:
Cellbanker 2
Host cell:
CHO-K1 β-Arrestin2
Transfection:
Expression vector containing full-length rat CNR2 cDNA (GenBank Accession Number NM_001164143.3) with FLAG tag sequence at N-terminus and ARRB2 cDNA (GenBank Accession Number NM_004313.3)
Recommended Storage:
Liquid nitrogen upon receiving
Propagation Medium: DME/F-12, 10% FBS, 10 ug/mL puromycin, 800 ug/ml G418
Stability: Stable for a minimum of 2 months in continuous culture
Data Sheet
Background: Cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2) is expressed in peripheral and immune tissues. CB2 in rodents is involved not only in processes of regulation of bone homeostasis but also in cannabinoid-induced central nerve system effects. This receptor can serve as potential therapeutic target in the treatment of various disorders affecting central nerve system or skeletal homeostasis. It was also demonstrated that CB2 receptor is involved in the reduction of chemotherapy-induced allodynia.
Application: Functional assays
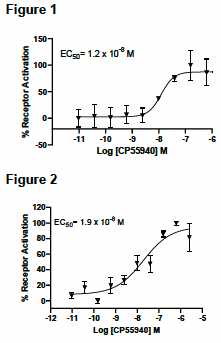
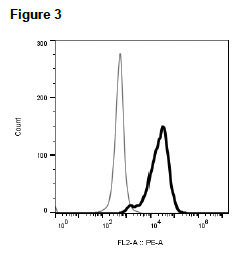
Figure 1. Dose-dependent stimulation from arrestin recruitment upon treatment with ligand, measured with MULTISCREEN™ β-Arrestin Assay Kit (Multispan MSBA01) Figure 2. Dose-dependent inhibition of forskolin-stimulated intracellular cAMP level upon treatment with ligand, measured with MULTISCREEN™ TR-FRET cAMP 1.0 No Wash Assay Kit (Multispan MSCM01). Figure 3. Receptor expression on cell surface measured by flow cytometry (FACS) using an anti-FLAG antibody. Thin line: parental cells; thick line: receptor-expressing cells.
References:
Raphael-Mizrahi and Gabet (2020). The cannabinoids effect on bone formation and bone healing. Curr. Osteoporos, 18(5), 433-438.
O’Hearn et al. (2017). Modulating the endocannabinoid pathway as treatment for peripherial neuropathic pain: a selected review of preclinical studies. Annals of palliative medicine, 6(Suppl 2), S209-S214.
Turcotte et al. (2016). The CB2 receptor and its role as a regulator of inflammation. Cell Mol Life Sci. 73(23):4449-4470.
