Product Information
Catalog Number:
H1165a
Lot Number:
H1165a-063011
Quantity:
1 vial (2 x 106) frozen cells
Freeze Medium:
Sigma Freezing Medium (C-6164)
Host cell:
HEK293T
Transfection:
Expression vector containing full-length human LTB4R cDNA (GenBank Accession Number NM_181657) with FLAG tag sequence at N-terminus
Recommended Storage:
Liquid nitrogen upon receiving
Propagation Medium: DMEM, 10% FBS, 1 μg/mL puromycin
Stability:
Stable for a minimum of two months in culture
Data Sheet
Background: Leukotriene B4 (LTB4) is a potent lipid mediator of allergic and inflammatory reactions, as well as a modulator of immune responses. Two types of plasma membrane receptors for LTB4 have been described on human neutrophils. The high-affinity human leukocyte LTB4 receptor, BLT1 (or LTB4R) mediates aggregation, chemotaxis, chemokinesis, and increased adherence to surfaces, whereas the low-affinity receptor mediates degranulation and increased oxidative metabolism. BLT1 mRNA is expressed in leukocytes and to a lesser degree in spleen and thymus. Studies in mice with disrupted BLT1 gene indicate a major role for BLT1 in acute inflammation and immediate hypersensitivity, as well as in leukocyte functions such as chemotaxis and firm adhesion to endothelium in response to LTB4.
Application: Functional assays
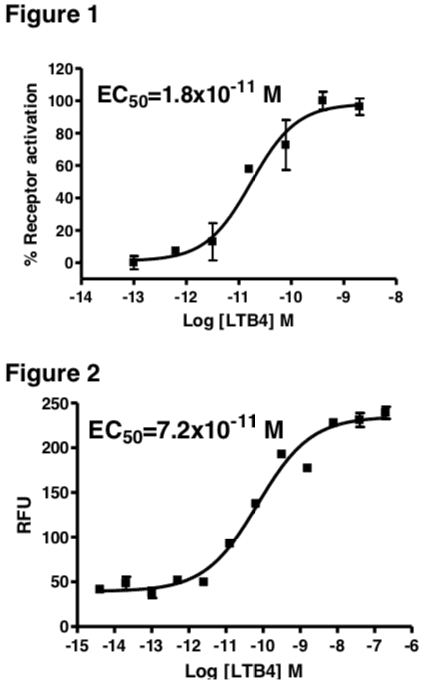
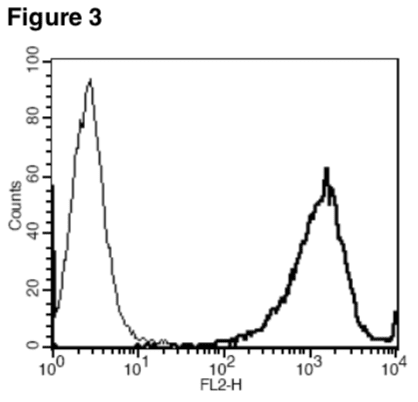
Figure 1. Dose-dependent inhibition of forskolin-stimulated intracellular cAMP level upon treatment with ligand, measured with MultiscreenTM TR-FRET cAMP 1.0 No Wash Assay Kit (Multispan MSCM01). Figure 2. Dose-dependent stimulation of calcium flux upon treatment with ligand, measured with MultiscreenTM Calcium 1.0 No Wash Assay Kit (Multispan MSCA01). Figure 3. Receptor expression on cell surface measured by flow cytometry (FACS) using an anti-FLAG antibody. Thin line: parental cells; thick line: receptor-expressing cells.
References:
Tager et al. (2000) BLTR mediates leukotriene B4-induced chemotaxis and adhesion and plays a dominant role in eosinophil accumulation in a murine model of peritonitis. J Exp Med 192:439.
Stankova et al. (2002) Modulation of leukotriene B4 receptor-1 expression by dexamethasone: potential mechanism for enhanced neutrophil survival. J Immunol 168:3570-3576
