Product Information
Catalog Number:
Cm1145-6
Lot Number:
C1145-6-062012
Quantity:
1 vial (2 x 106) frozen cells
Freeze Medium:
Sigma Freezing Medium (C-6164)
Host cell:
RH7777
Transfection:
Expression vector containing full-length mouse LPA5 cDNA (GenBank Accession Number: NM_001163268.1) with FLAG tag sequence at N-terminus
Recommended Storage:
Liquid nitrogen upon receiving
Propagation Medium: DMEM, 10% FBS, 3 μg/mL puromycin
Stability:
In progress
Data Sheet
Background: LPA5 (GPR92) represents a putative orphan G protein coupled receptor with unknown functions. The mouse LPA5 receptor gene has an 81% homology to the human ortholog. Research has shown LPA5 to be expressed in the mouse intestine and upon stimulation with LPA, activates Na+/H+ exchanger 3 and stimulates sodium and fluid absorption. ESTs for LPA5 have been isolated from human normal brain, testis, and tonsil B-cell libraries and from a human blood cancer cell library (pre-B cell). LPA5 protein contains 372 amino acids and shared 36 to 40% sequence identity in the transmembrane regions with the G protein-coupled purinergic receptor P2Y5 (P2RY5), GPR23, and GPR17.
Application: Functional assays
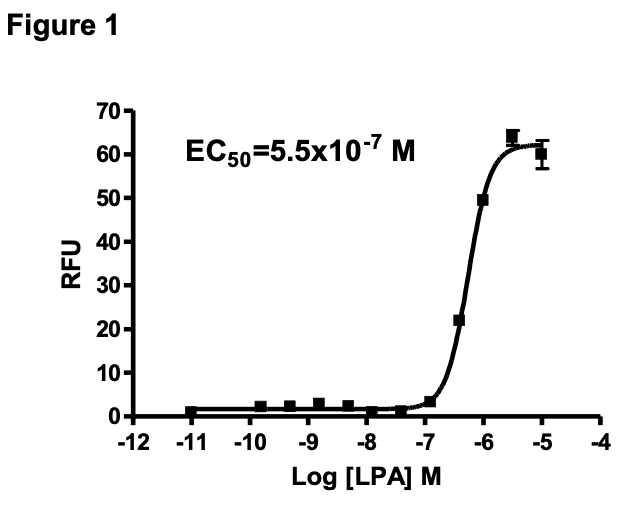
Figure 1. Dose-dependent stimulation of calcium flux upon treatment with ligand, measured with MultiscreenTM Calcium 1.0 No Wash Assay Kit (Multispan MSCA01). Figure 2. Receptor expression on cell surface measured by flow cytometry (FACS) using an anti-FLAG antibody. Thin line: parental cells; thick line: receptor-expressing cells.
References:
Lee et al. (2001) Discovery and mapping of ten novel G protein coupled receptor genes. Gene 275:83-91.
White et al. (2000) Autosomal dominant hypophosphataemic rickets is associated with mutations in FGF23. Nat Genet 26:345-348.
Lee et al. (2006) GPR92 as a new G12/13- and Gq-coupled lysophosphatidic acid receptor that increases cAMP, LPA5. J Biol Chem 281:23589-23597.
Yoo et al. (2011) Lysophosphatidic acid 5 receptor induces activation of Na+/H+ exchanger 3 via apical epidermal growth factor receptor in intestinal epithelial cells. American Journal of Physiology Cell Physiology Vol. 301 no. 5 C1008-C1016.
